Economics and Marketing
Estimated Income and Cost of Goat Farming Unit
Estimated income and expenditure can be found as the cost varies with the region and socio-economic background of the farmers or entrepreneurs. It is advised to invest your own money without taking any kind of loan.
| Disease | A view of the balance sheets |
|---|---|
| A) | Non-recurring expenditure |
| 1. | Construction of shed (Local materials should be preferred) |
| 2. | Storage room and laborer's room |
| 3. | Chaff cutter |
| 4. | Purchase of goats (male and female). |
| 5. | Insurance |
| 6. | Land and water facilities |
| B) | Recurring expenditure |
| 1. | Production of green fodder |
| 2. | Dry fodder |
| 3. | Concentrate feed/mixed ration (preferably homemade) |
| 4. | Veterinary medicines |
| 5. | Expenditure of laborers (family members is preferable) |
| 6. | Depreciation on shed |
| 7. | Depreciation on equipments |
| 8. | Interest on loan |
| C) | Income |
| 1. | Sale of milk (if possible) |
| 2. | Manure sale |
| 3. | Sale of gunny bags |
| 4. | Sale of Bucks |
| 5. | Sale of kids |
| Net Profit = Total Income - Recurring Expense |
Marketing of Goat Products
With the increasing demand for goat products, they are gaining popularity for their unique flavor, health benefits, and sustainability. Goat farming has a lower environmental impact than traditional livestock farming, making it a viable option for consumers looking for eco-friendly and sustainable food options.
Marketing Channels

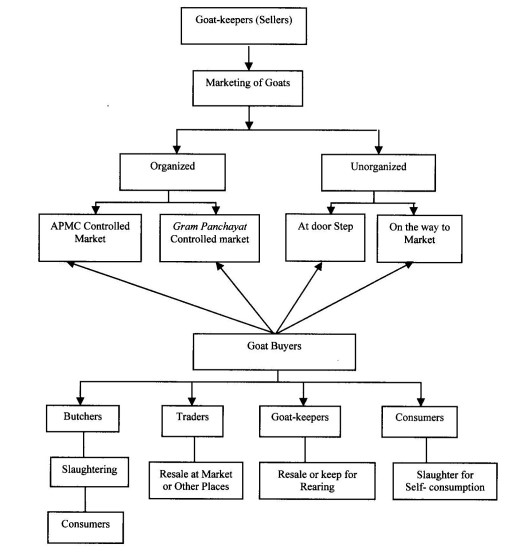
The demand for goat products is rising, creating new possibilities for farmers and merchants since goat products are becoming more popular and have unique health benefits. Goat milk, cheese and meat (chevon) are sought after by consumers looking for high quality, sustainably sourced and healthy options. Goat products are also favoured by those with lactose intolerance or sensitivity, providing a wider consumer base.

